wheatstone bridge calculator
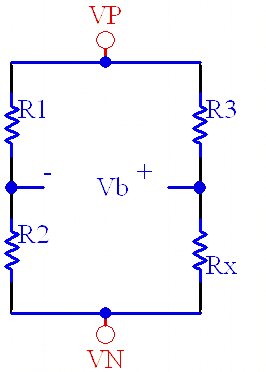
a wheatstone bridge (also known as a one-arm bridge) is an instrument that can accurately measure resistance. figure 3-13 shows a general wheatstone bridge. resistors r1, r2, r3, and r4 are called the four arms of the bridge, and g is a galvanometer to check whether there is current in the branch where it is located. when no current flows through g, the bridge is said to be balanced. when balanced, the resistance values of the four arms satisfy a simple relationship, and this relationship can be used to measure resistance.
the bridge voltage is calculated as follows:
VB= Vin*[Rx/(R3+Rx)- R2/(R1+R2)]
if r3=r1, and rx= r2+delta, then
VB= Vin*[ (R2+delta)/(R1+R2+delta)-R2/(R1+R2)]
now, if we assumedeltais smaller than r1 + r2, then
VB= ~ Vin*[delta/(R1+R2)]
therefore, we can see that the bridge voltage is approximately proportional to the errordelta, divided by the sum of resistances divided by one side.
since the bridge voltage we can calculate it as an unknown resistor value.
(R1+R2)*(R3+Rx)*VB/Vin= Rx*(R1+R2)+ R2*(R3+Rx)
Rx*(R1+R2)*VB/ Vin + R3* (R1+R2)VB/Vin= Rx*R1+Rx*R2 - R2*R3- Rx*R2
Rx*R1 - Rx*(R1+R2)*VB/ Vin = R2*R3 + R3* (R1+R2)VB/Vin
Rx = (R2*R3 + R3* (R1+R2)VB/Vin )/ (R1- (R1+R2)*VB/ Vin)
